Many factors can contribute to excess weight gain
including eating patterns, physical activity levels,
and sleep routines. Social
determinants of health, genetics, and taking certain medications also
play a role.
Obesity is a complex issue with many
causes. It's caused when extra calories are stored in the body as
fast
If you consume high amounts of energy, particularly found in high fat
and high sugar foods, and do not use all of the energy through physical activity,
much of the extra energy will be stored in the body as fast
What is obesity?
Obesity is a complex, chronic disease with
several causes that lead to excessive body fat and sometimes, poor health. Body
fat itself is not a disease, of course. But when your body has too much extra
fat, it can change the way it functions. These changes are progressive, can
worsen over time, and they can lead to adverse health effects.
The good news is that you can improve your
health risks by losing some of your excess body fat. Even small changes in
weight can have a big impact on your health. Not every weight loss method works
for everyone. Most people have tried to lose weight more than once. And keeping
the weight off is just as important as losing it in the first place.
What are the
three types of obesity?
Healthcare providers classify obesity into
class types based on how severe it is. They use BMI to do it. If your BMI is
between 25.0 and 29.9 kg/m², they put you in the overweight category. There are
three general classes of obesity that healthcare providers use to evaluate what
treatments may work best for each person. They include:
- Class I obesity: BMI 30 to
<35 kg/m².
- Class II obesity: BMI 35 to
<40 kg/m².
- Class III obesity: BMI 40+
kg/m².
How does
obesity affect my body?
Obesity affects your body in many ways. Some
are simply the mechanical effects of having more body fat. For example, you can
draw a clear line between extra weight on your body and extra pressure on your
skeleton and joints. Other effects are more subtle, such as chemical changes in
your blood that increase your risk for diabetes, heart disease and stroke.
Some effects are still not well understood.
For example, there is an increased risk of certain cancers with obesity. We
don’t know why, but it exists. Statistically, obesity increases your risk of
premature death from all causes. By the same token, studies show that you can
significantly improve these risks by losing even a small amount of weight (5%
to 10%).
What are the symptoms of obesity?
There are no
specific symptoms associated with obesity. A doctor may diagnose obesity based
on the following factors:
- excess amounts of abdominal (visceral) fat that are higher than the amounts of body fat in other are
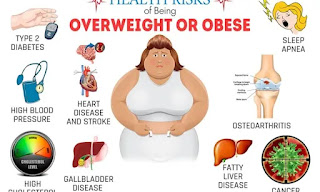
Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity
·
All-causes of death
(mortality).
·
High blood pressure
(hypertension).
·
High LDL cholesterol,
low HDL cholesterol, or high levels of triglycerides (dyslipidemia).
·
Type 2 diabetes.
·
Coronary heart
disease.
·
Stroke.
·
Gallbladder disease.
How is obesity
classified?
The following Classes
trusted source are used for adults who are at least 20 years old:
|
BMI |
Class |
|
18.5 or under |
Underweight |
|
18.5 to <25 |
“normal” weight |
|
25 to <30 |
Overweight |
|
30 to <35 |
class 1 obesity |
|
35 to <40 |
class 2 obesity |
|
40 or over |
class 3 obesity (also known as morbid, extreme, or
severe obesity) |
What is childhood obesity?
For a doctor to diagnose obesity
in a child over 2 years old or a teen their BMI has to be at or above
the 95th percentage trusted source A BMI at or above the 95th percentile is
higher than the BMI of 95% of people with the same age and sex assigned at
birth.
|
Percentile range of BMI |
Class |
|
>5% |
underweight |
|
5% to <85% |
“normal” weight |
|
85% to <95% |
overweight |
|
95% or over |
Obesity |
From 2015 to 2016, 18.5%
trusted source (or about 13.7 million) of U.S. youth between 2 and 19
years old
What are the types of
weight loss surgery?
Weight loss surgery is commonly
called bariatric surgery.
This type of surgery limits how
much food you can comfortably eat or prevents your body from absorbing food and
calories. Sometimes it can do both.
Weight loss surgery isn’t a quick
fix. It’s a major surgery and can have serious risks. Afterward, people who
undergo surgery will need to change how they eat and how much they eat, or they
risk getting sick.
However, nonsurgical options
aren’t always effective at helping people with obesity lose weight and reduce
their risk of comorbidities.
Types of weight loss surgery
include:
- Gastric bypass
surgery: In
this procedure, a surgeon creates a small pouch at the top of your
stomach that connects directly to your small intestine. Food and liquids
go through the pouch and into the intestine, bypassing most of the
stomach. It’s also known as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) surgery.
- Laparoscopic
adjustable gastric banding (LAGB): LAGB separates your stomach
into two pouches using a band.
- Gastric sleeve
surgery: This procedure removes
part of your stomach.
- Biliopancreatic
diversion with duodenal switch: This procedure removes most of
your stomach.





.png)

1 Comments
Aad baan ugu farahsanahay in aan manta wax badan ka faaido obesity BMI
ReplyDelete